Geography
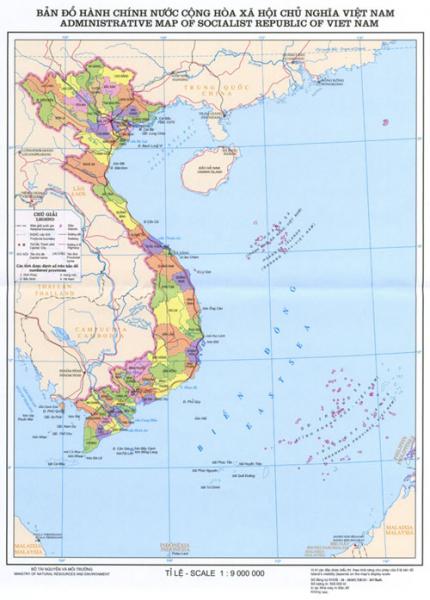
Viet Nam is located on the Indochina peninsula in Southeast Asia. It has a long land border of 4,550 km, bordering China to the North, Laos and Cambodia to the West, and the Eastern Sea (South China Sea) of Pacific Ocean to the East. On the map, Viet Nam is an S-shaped strip of land, stretching from 23°23’ to 8°27’ North latitude. The country’s total length is 1,650 km from the northernmost point to the southernmost point. Its width, from the Eastern coast to the Western border, is about 500 km at the widest part and about 50 km at the narrowest part.
The country’s diverse topography consists of hills, mountains, deltas, coastline and continental shelf, reflecting the long history of geology and topography formation in a monsoon, humid climate and strong weather exposure. The topography is lower from the Northwest to the Southeast, which can be clearly observed in the flows of major rivers.
Three quarters of Viet Nam’s territory are made up of low mountains and hilly regions. Regions with elevation lower than 1,000 meters above sea level make up 85% of the territory. Mountainous regions over 2,000 meters above sea level account for only 1%. Hills and mountain ranges form a large bow, 1,400 km in length from the Northwest to the Southeast, heading towards the Eastern Sea. The highest mountain ranges are all located in the West and Northwest with the peak of Fansipan (3,143 meters), the highest in Indochina. Nearer to the Eastern Sea, the mountain ranges lower and usually end with a coastal strip of lowland. From Hai Van Pass to the South, the topography is simpler. Long limestone mountain ranges are replaced by large granite mountains followed by a vast plateau known as the Central Highlands behind Truong Son Range to the East.
Only one-fourth of the Vietnamese territory is covered by deltas, separated into regions by mountains and hills. There are two major deltas with fertile arable land in Viet Nam, the 16,700 sq km Red River Delta, locally known as the Northern Delta, and the 40,000 sq km Mekong River Delta, or the Southern Delta. Between these two major deltas is a chain of small and narrow deltas along the Central coast from the Ma River basin in Thanh Hoa Province to Phan Thiet with the total area of 15,000 sq km.
Viet Nam faces the Eastern Sea to the East and the Gulf of Thailand to the South and Southwest. The country has a long coastline of 3,260 km running from Mong Cai in the North to Ha Tien in the Southwest. Viet Nam’s territorial waters in the Eastern Sea extend to the East and Southeast, including the continental shelf, islands and archipelagoes. There is a group of around 3,000 islets belonging to Viet Nam in the Tonkin Gulf, including Ha Long Bay, Bai Tu Long Bay, Cat Hai, Cat Ba and Bach Long Vi Island. Farther in the Eastern Sea are Hoang Sa Archipelago (Paracel Islands) and Truong Sa Archipelago (Spratly Islands). To the West and the Southwest, there are groups of islands including Con Son, Phu Quoc and Tho Chu.



